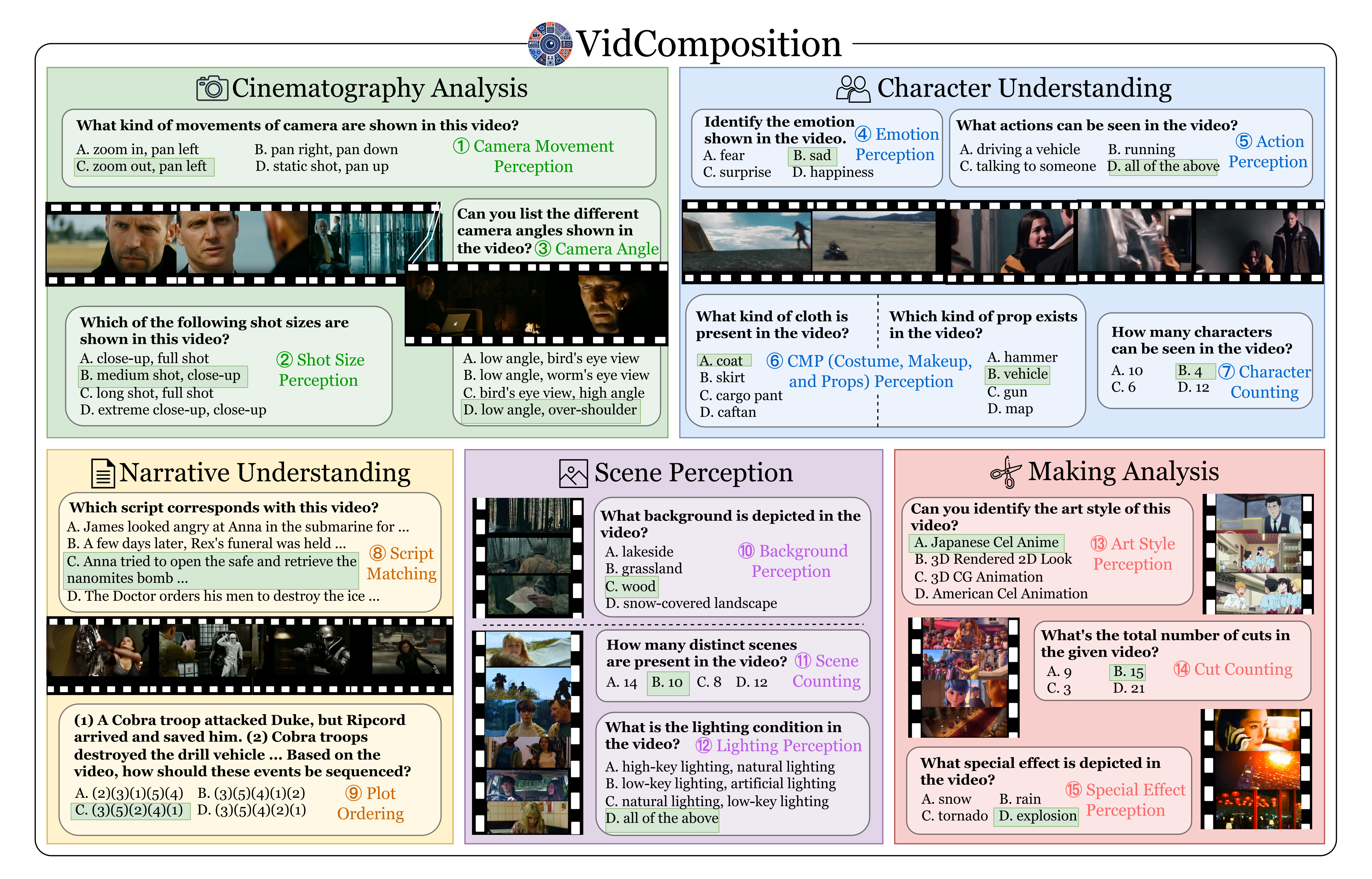
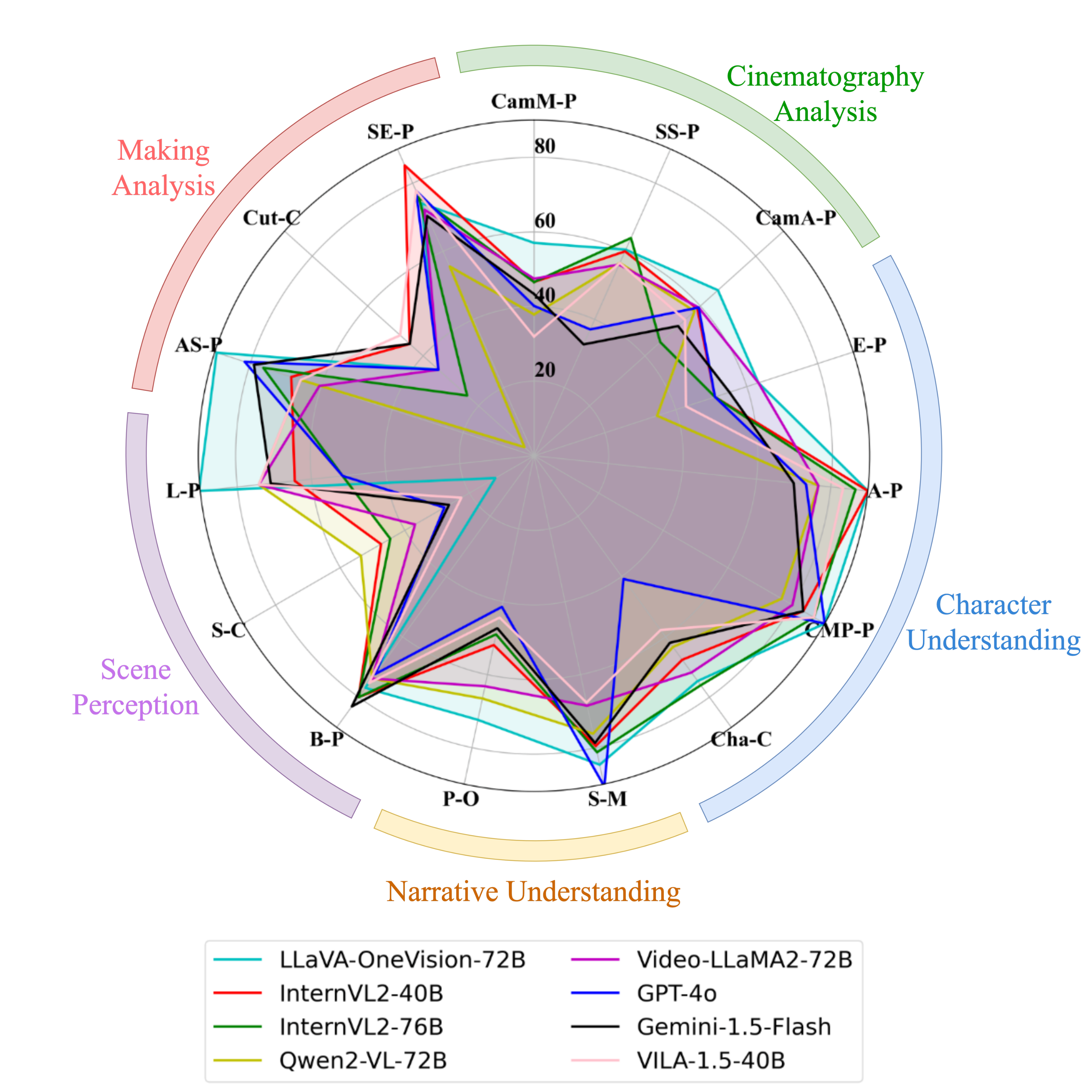
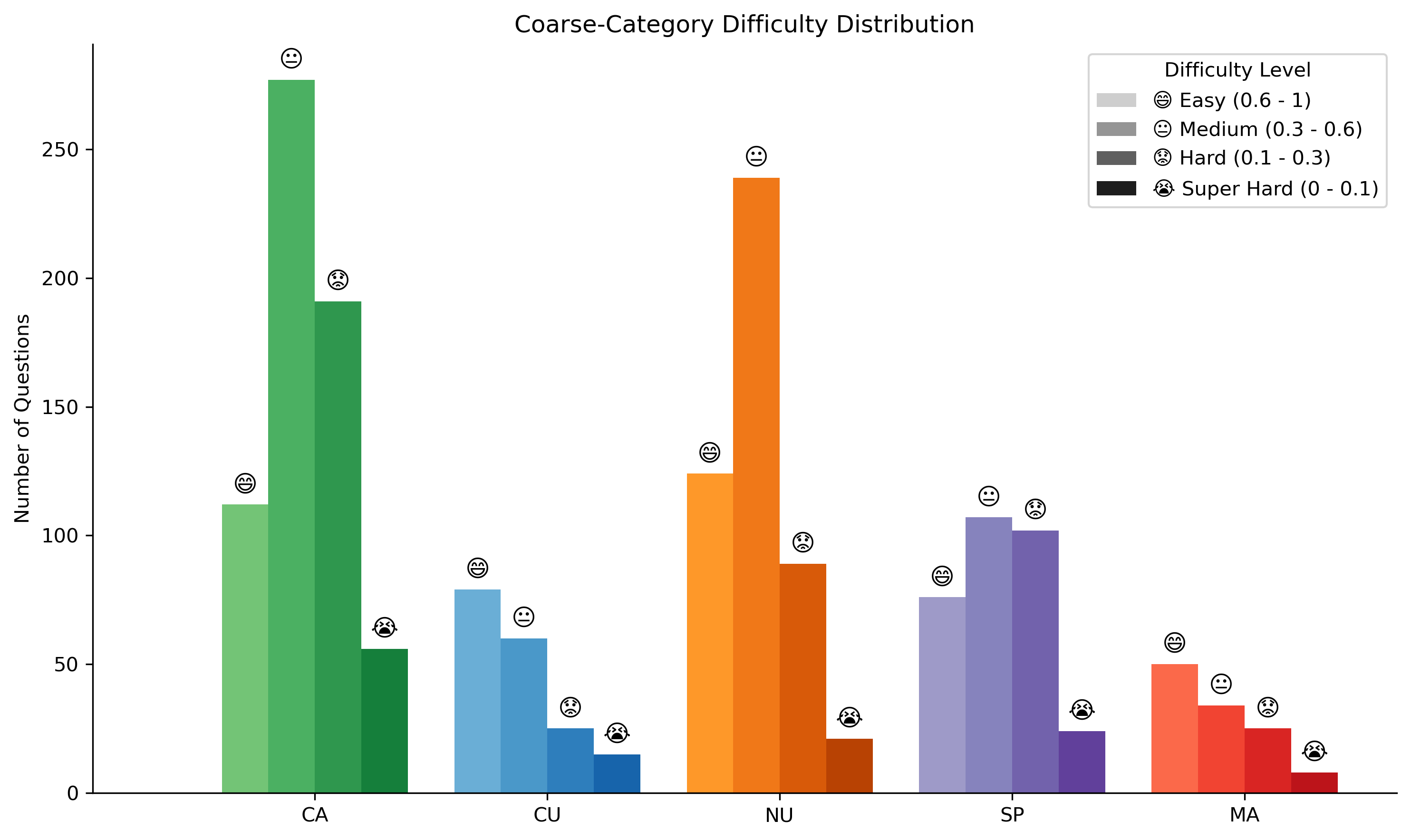
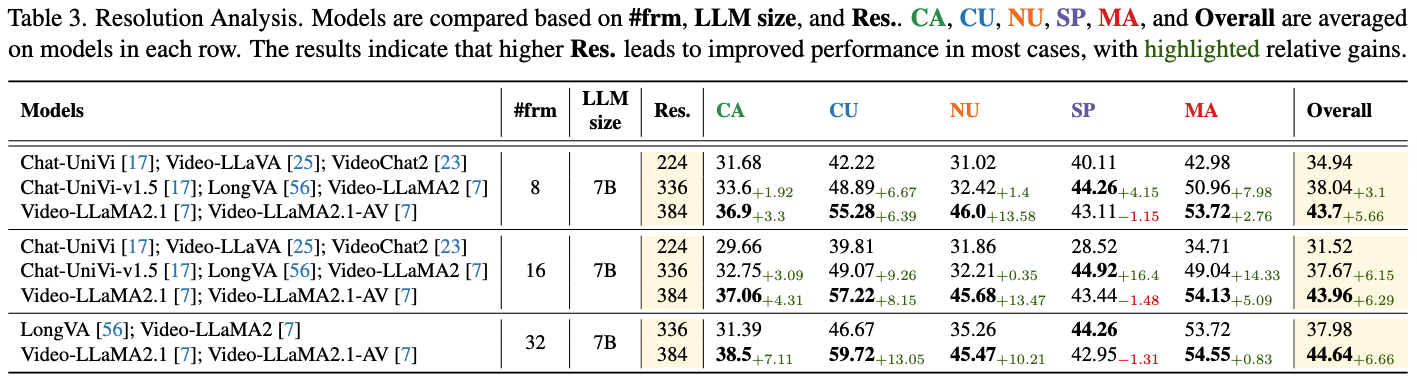
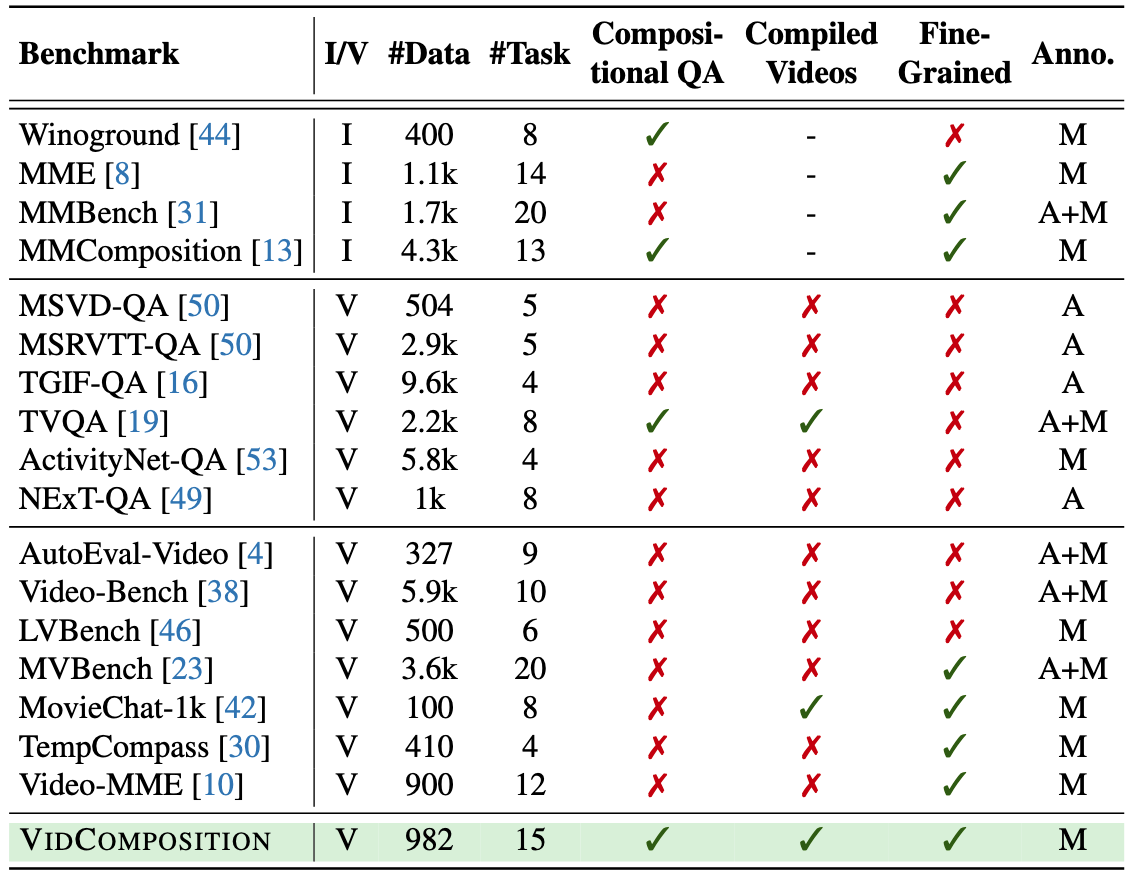
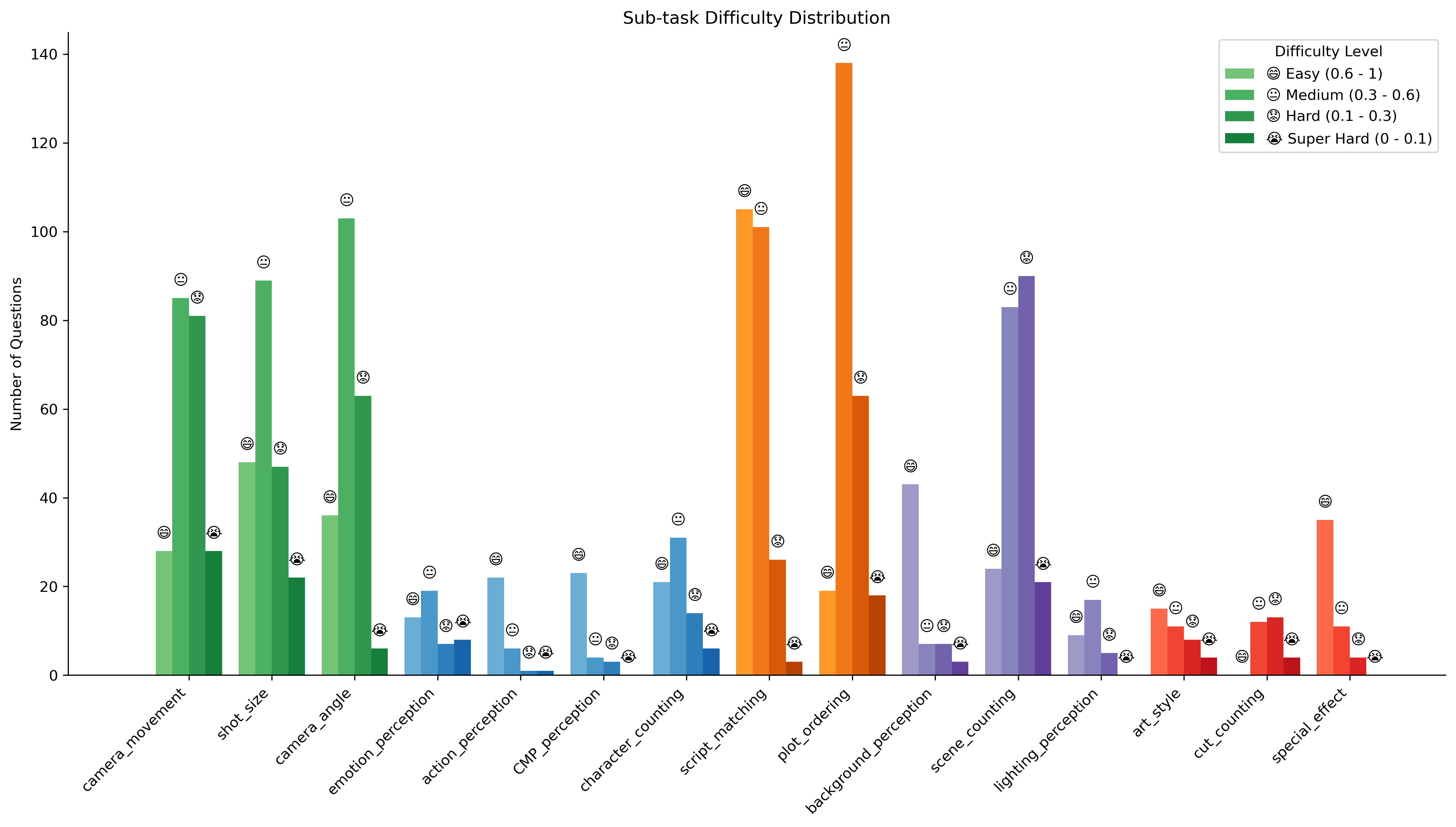
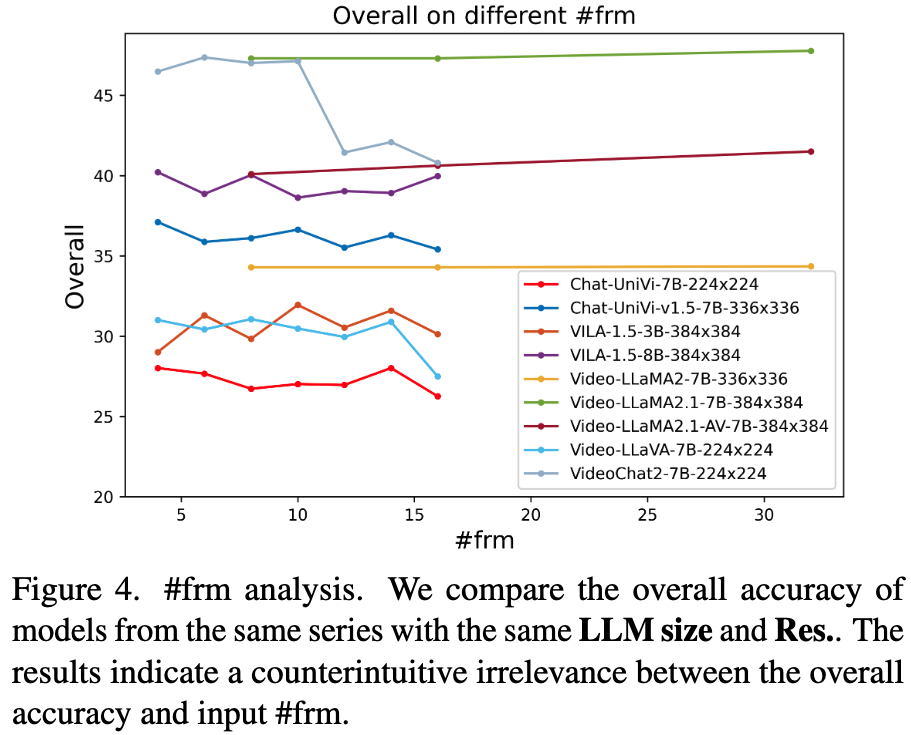
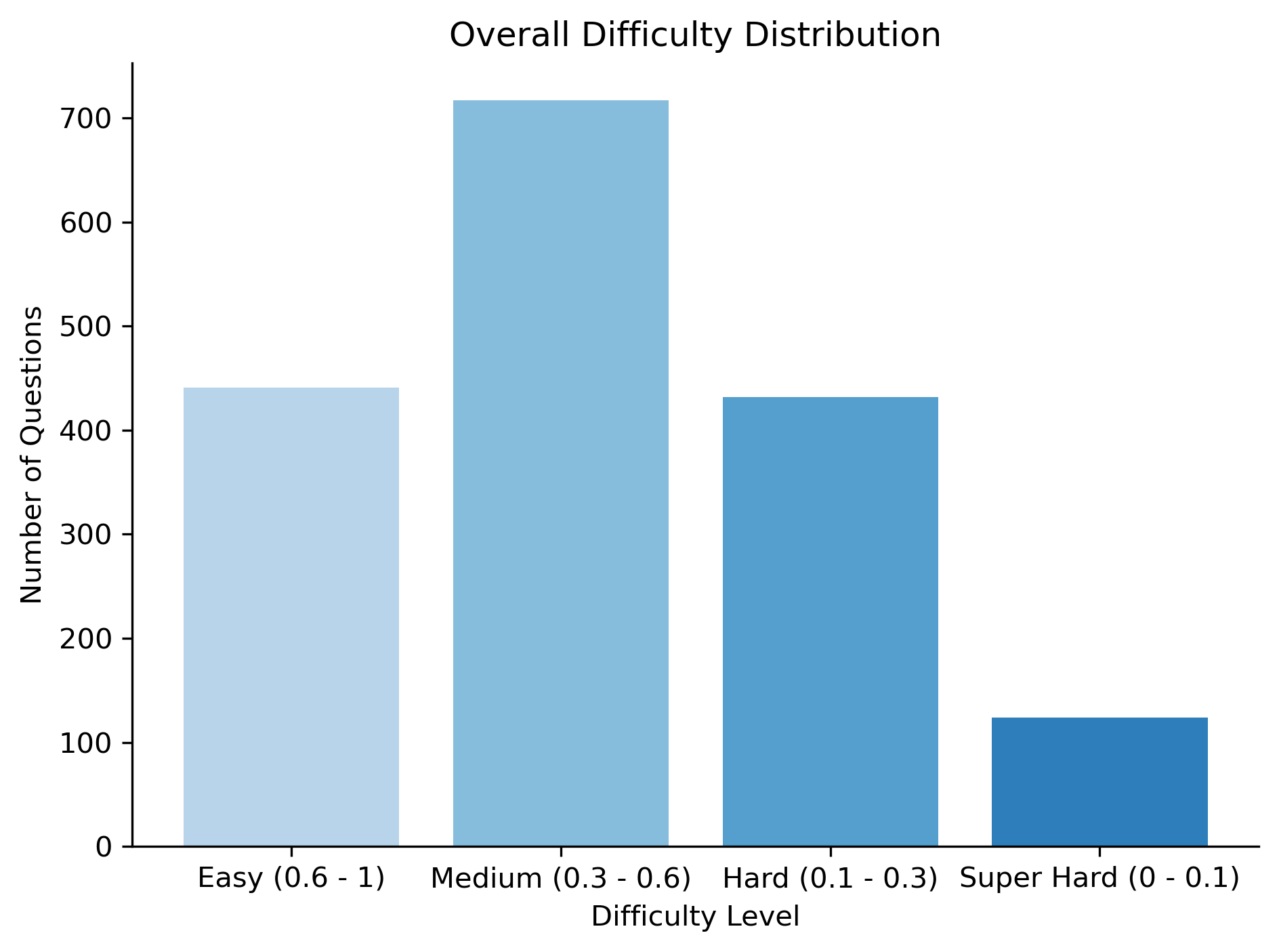
By default, this leaderboard is sorted by overall results. To view other sorted results, please click on the corresponding cell. Colored rows indicate closed-source models/APIs.
| # | Model | LLM Params |
Frames | Date | Overall (%) | CA (%) | CU (%) | NU (%) | SP (%) | MA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🥇 |
Gemini-2.5-flash-preview
|
- | 1fps | 2025/05/05 | 69.11 | 58.95 | 73.33 | 86.11 | 55.74 | 81.82 |
| 🥈 |
LLaVA-OneVision-72B
Bytedance & NTU S-Lab |
72B | 32 | 2024/11/10 | 63.31 | 61.18 | 76.67 | 78.32 | 33.77 | 69.42 |
| 🥉 |
InternVL2-40B
Shanghai AI Lab |
34B | 16 | 2024/10/31 | 60.73 | 54.95 | 69.44 | 65.47 | 56.07 | 70.25 |
| 4 |
InternVL2-76B
Shanghai AI Lab |
70B | 16 | 2024/10/31 | 58.73 | 51.92 | 72.78 | 64.84 | 52.79 | 63.64 |
| 5 |
Qwen2-VL-72B
Alibaba |
72B | 2fps | 2024/11/02 | 58.68 | 50.48 | 60.00 | 71.16 | 60.00 | 46.28 |
| 6 |
Video-LLaMA2-72B
DAMO Academy & Alibaba Group |
72B | 32 | 2024/11/07 | 58.62 | 54.15 | 71.67 | 65.68 | 48.52 | 59.50 |
| 7 |
InternVL2-8B
Shanghai AI Lab |
7B | 16 | 2024/10/30 | 54.63 | 57.03 | 62.78 | 53.68 | 45.57 | 56.20 |
| 8 |
GPT-4o
OpenAI |
- | 1fps | 2024/11/03 | 52.93 | 45.37 | 57.22 | 65.68 | 39.67 | 68.60 |
| 9 |
Gemini-1.5-Flash
|
- | 1fps | 2024/11/04 | 52.40 | 42.65 | 65.00 | 62.74 | 42.95 | 66.94 |
| 10 |
mPLUG-Owl3
Alibaba Group |
7B | 16 | 2024/12/09 | 52.29 | 48.72 | 63.33 | 60.21 | 39.01 | 56.19 |
| 11 |
VILA-1.5-40B
NVIDIA & MIT |
34B | 14 | 2024/11/02 | 51.23 | 47.28 | 62.78 | 55.79 | 39.02 | 66.94 |
| 12 |
GPT-4o mini
OpenAI |
- | 1fps | 2024/11/03 | 50.23 | 44.41 | 53.89 | 60.21 | 38.69 | 64.46 |
| 13 |
Gemini-1.5-Pro
|
- | 1fps | 2024/11/04 | 49.36 | 45.37 | 67.22 | 41.89 | 48.52 | 74.38 |
| 14 |
Qwen2-VL-7B
Alibaba |
7B | 2fps | 2024/10/28 | 49.30 | 34.35 | 56.67 | 61.05 | 57.38 | 48.76 |
| 15 |
Oryx-7B
Tsinghua University & Tencent & S-Lab, NTU |
7B | 16 | 2024/11/07 | 48.77 | 48.40 | 67.22 | 41.47 | 50.49 | 47.11 |
| 16 |
Gemini-1.5-Flash-8B
|
8B | 1fps | 2024/11/04 | 48.59 | 48.56 | 48.33 | 52.63 | 39.02 | 57.02 |
| 17 |
Video-LLaMA2.1
Shanghai AI Lab & CUHK & SenseTime |
7B | 32 | 2024/10/28 | 47.77 | 39.94 | 60.56 | 52.84 | 46.23 | 52.89 |
| 18 |
VideoChat2
Shanghai AI Lab |
- | 10 | 2024/11/05 | 47.13 | 38.98 | 60.00 | 45.47 | 56.07 | 53.72 |
| 19 |
InternVL2-26B
Shanghai AI Lab |
20B | 16 | 2024/10/30 | 46.42 | 40.10 | 63.89 | 51.16 | 38.36 | 54.55 |
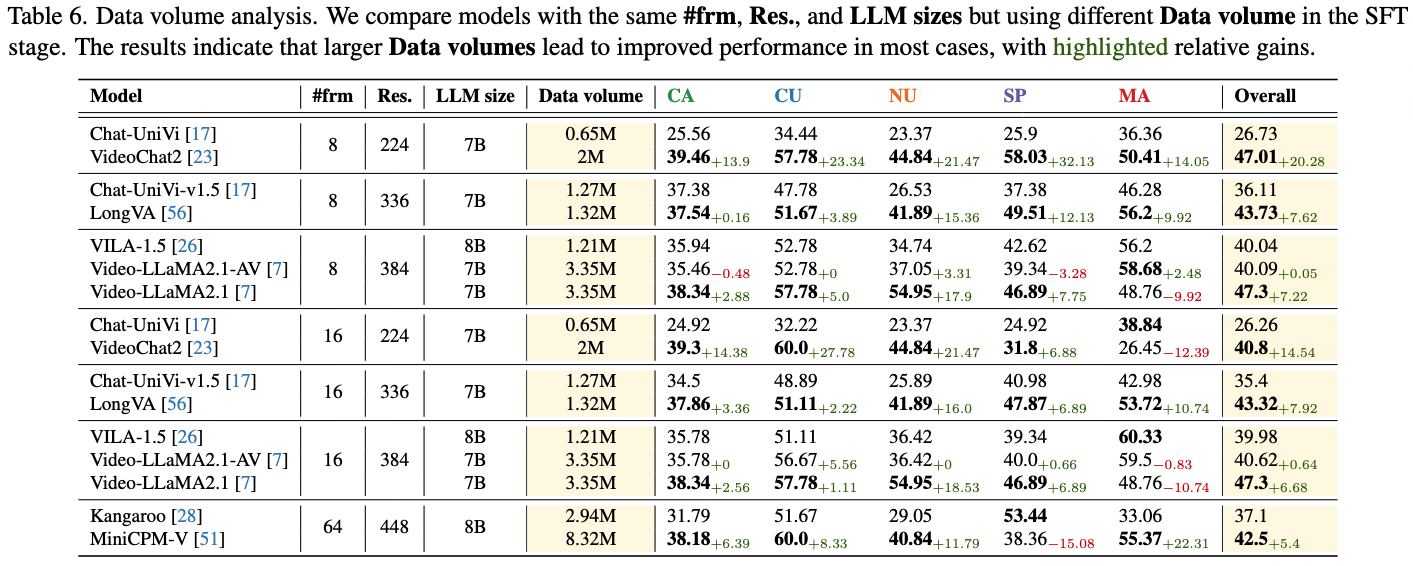
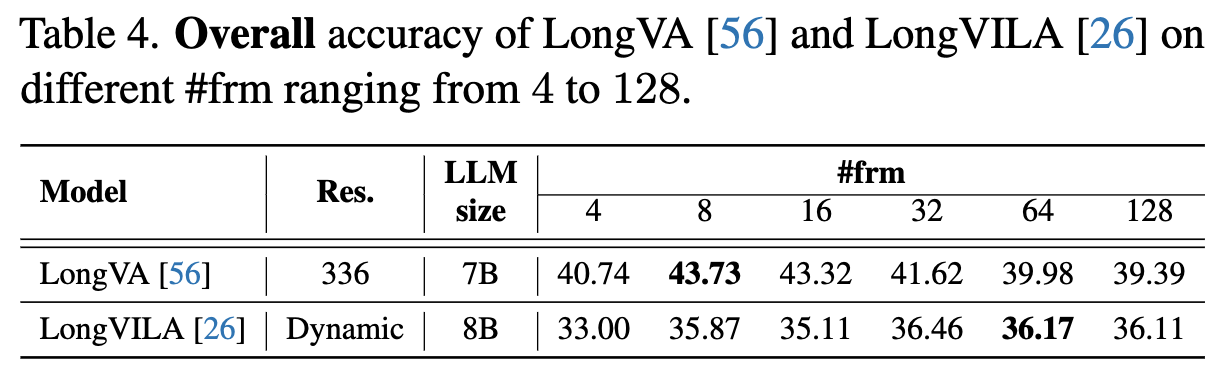
| 20 |
LongVA
NTU S-Lab |
7B | 8 | 2024/10/29 | 43.73 | 37.54 | 51.67 | 41.89 | 49.51 | 56.20 |
| 21 |
MiniCPM-V2.6
OpenBmB |
8B | 64 | 2024/11/01 | 42.50 | 38.18 | 60.00 | 40.84 | 38.36 | 55.37 |
| 22 |
InternVL2-4B
Shanghai AI Lab |
3.8B | 16 | 2024/10/30 | 41.68 | 32.11 | 51.67 | 44.00 | 48.85 | 48.76 |
| 23 |
Video-LLaMA2.1-AV
DAMO Academy & Alibaba |
7B | 32 | 2024/11/06 | 41.50 | 37.06 | 58.89 | 38.11 | 39.67 | 56.20 |
| 24 |
VILA-1.5-8B
Nvidia |
8B | 4 | 2024/10/29 | 40.21 | 36.26 | 51.67 | 33.68 | 45.25 | 56.20 |
| 25 |
GPT-4-turbo
OpenAI |
- | 1fps | 2023/11/03 | 39.86 | 31.79 | 46.67 | 45.47 | 37.70 | 54.55 |
| 26 |
LongLLaVA
Amazon |
7B | 64 | 2024/11/01 | 38.45 | 30.83 | 47.78 | 40.21 | 43.61 | 43.80 |
| 27 |
Chat-UniVi-v1.5
PKU |
7B | 4 | 2024/11/06 | 28.02 | 28.91 | 31.11 | 25.26 | 23.93 | 39.67 |
| 28 |
Kangaroo
Meituan & UCAS |
8B | 64 | 2024/10/31 | 37.10 | 31.79 | 51.67 | 29.05 | 53.44 | 33.06 |
| 29 |
InternVL2-2B
Shanghai AI Lab |
1.8B | 16 | 2024/11/01 | 36.75 | 24.28 | 54.44 | 35.16 | 47.54 | 53.72 |
| 30 |
LongVILA
Nvidia |
8B | 32 | 2024/11/03 | 36.46 | 33.55 | 49.44 | 28.84 | 37.05 | 60.33 |
| 31 |
AuroraCap
University of Washington |
7B | 8 | 2024/10/28 | 36.28 | 38.98 | 45.00 | 28.63 | 32.13 | 49.59 |
| 32 |
Qwen2-VL-2B
Alibaba |
2B | 2fps | 2024/11/02 | 36.17 | 25.08 | 47.22 | 37.05 | 47.54 | 44.63 |
| 33 |
Video-LLaMA2-7B
DAMO Academy & Alibaba |
7B | 32 | 2024/10/28 | 34.35 | 25.88 | 47.78 | 28.84 | 45.90 | 50.41 |
| 34 |
VILA-1.5-3B
Nvidia |
3B | 10 | 2024/10/30 | 31.95 | 30.03 | 42.78 | 18.32 | 42.95 | 51.24 |
| 35 |
Video-LLaVA
PKU |
7B | 8 | 2024/11/01 | 31.07 | 30.03 | 34.44 | 24.84 | 36.39 | 42.15 |
| 36 |
Chat-UniVi
PKU |
7B | 4 | 2023/10/28 | 28.02 | 28.91 | 31.11 | 25.26 | 23.93 | 39.67 |
| 37 |
InternVL2-1B
Shanghai AI Lab |
0.5B | 16 | 2024/10/30 | 26.61 | 24.12 | 28.33 | 26.53 | 29.84 | 28.93 |
| 38 | RANDOM | - | - | 2024/10/28 | 25.28 | 25.70 | 24.28 | 25.12 | 24.62 | 26.61 |